
AIIMS attack is one in 1.9 mn hack attempts on India's healthcare sector in 2022


The recent cyberattack on the All India Medical Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) may have only been the tip of the iceberg for attacks on India's healthcare sector. According to a report by cybersecurity think-tank the CyberPeace Foundation and security consultancy Autobot Infosec Private Ltd, the healthcare sector in India had faced 1.9 million cyber attacks till November 28 this year. The attacks came from 41,181 unique IP addresses, which were traced back to Vietnam, Pakistan, and China, the report said.
Last week, India’s top government-run hospital, AIIMS in New Delhi, was hit by a massive cyberattack forcing the medical institution to shut down many of its servers and switch to manual operations. AIIMS, which had earlier announced plans to digitize all services by April 2023, refuted reports claiming that the hackers had asked for a ransom of ₹200 crore.
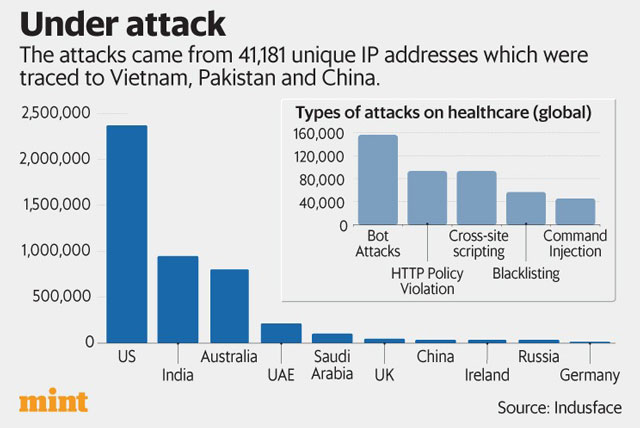
According to Tata Capital-backed security firm IndusFace, India was the second most targeted country in terms of attacks on the healthcare sector. The company, too, found that of the 1 million attacks it detected on its healthcare customers every month in 2022, 278,000 were from India.
Around 80% of these attacks targeted internal Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS), customer service portals, ticketing systems and developer tools, the firm told Mint.
“The attack on AIIMS servers is extremely unfortunate as it affects halthcare delivery to people in urgent need of care. At the same time, it underscores how cybersecurity has to be integrated holistically into the healthcare landscape in India,” said Ashish Tandon, founder and chief executive of Indusface, adding that it is time for healthcare firms to revamp their approach to security.
The data on threats released by CyberPeace Foundation was generated through its e-Kawach program, which uses specialized threat sensors to capture internet traffic and analyse real-time cyber attacks faced by organizations. It can also categorize these attacks by location.
The report also showed that attackers mostly targeted vulnerable internet-facing systems, including remote desktop protocol (RDP), vulnerable server message blocks (SMB) and database services, and old Windows server platforms.
RDP attacks are those where hackers gain remote access to an organization or person’s computer. They have increased significantly since the pandemic, as more users started using legitimate remote access protocols to access office PCs while sitting at home, etc. Vulnerabilities in software used for such remote access tasks can allow hackers to get in.
Another common type of attack includes brute force and dictionary attacks to exploit file transfer protocol (FTP), Digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM), MYSQL (database management system). Attackers use such attacks to steal sensitive patient data, including medical images of scans and diagnostic databases. FTP, DICOM and MySQL are technologies used in transferring files over networks, storing medical data, and database management, respectively.
Further, CyberPeace’s report said that the objective behind most of the attacks was to inject a malicious payload into the network of the healthcare company and trigger ransomware attacks. The company’s sensors found 1,527 unique payloads (the virus of worm used to infect a computer) had been used.
To be sure, India isn’t the only country where healthcare firms are under fire. Cyberattacks on healthcare have grown across the world as more hospitals and healthcare services providers are moving their operations and databases online. According to cybersecurity firm CheckPoint Research, healthcare suffered the highest number of ransomware attacks globally during the September quarter of 2022.
